-
Bishop, Laura; Høffding, Simon; Laeng, Bruno & Lartillot, Olivier
(2023).
Mental effort and expressive interaction in expert and student string quartet performance.
-
Bishop, Laura; Høffding, Simon; Lartillot, Olivier Serge Gabriel & Laeng, Bruno
(2023).
Mental effort and expressive interaction in expert and student string quartet performance.
-
Laeng, Bruno & Vemøy, Silje Kilmork
(2022).
Pupillens hemmeligheter.
[Radio].
radio.nrk.no.
Show summary
Pupillens hemmeligheter
At øynenes er sjelens speil, er kanskje en mer presis observasjon enn mange er klar over. Den sorte pupillen kan fortelle en hel del om oss mennesker, for eksempel om hvordan vi har det.
-
Akca, Merve; Bishop, Laura; Vuoskoski, Jonna Katariina & Laeng, Bruno
(2022).
Tracing the Temporal Limits of Auditory Information Processing with Pupillometry.
-
van Otterdijk, Marieke; Saplacan, Diana; Laeng, Bruno & Torresen, Jim
(2022).
Explorative Study on Human Intuitive Responses to Observing
Expressive Robot Behavior.
-
Bishop, Laura & Laeng, Bruno
(2022).
Expertise modulates the relationship between musical demands and mental effort.
-
Spiech, Connor; Hope, Mikael; Câmara, Guilherme Schmidt; Sioros, Georgios; Endestad, Tor & Laeng, Bruno
[Show all 7 contributors for this article]
(2022).
PredicTAPbility: Sensorimotor Synchronization Increases Groove.
-
Bishop, Laura; Gonzalez Sanchez, Victor Evaristo; Laeng, Bruno; Jensenius, Alexander Refsum & Høffding, Simon
(2021).
Social context affects head motion and gaze in string quartet rehearsal and concert performance.
-
Spiech, Connor; Laeng, Bruno; Sioros, George; Danielsen, Anne & Endestad, Tor
(2021).
More Than Meter’s The Eye: Divergent Roles of Pickups and Syncopation in Groove.
-
-
Minami, Tetsuto & Laeng, Bruno
(2018).
Brightness perception while looking up or down.
-
Laeng, Bruno
(2018).
The "face race lightness illusion": An effect of the eyes and pupils? .
-
Sato, Fumiyaki; Laeng, Bruno; Nakauchi, Shigeki & Minami, Tetsuto
(2018).
Pupil dilation reflects "Viewing from above bias" in the effort to control perception.
-
Suzuki, Yuta; Minami, Tetsuto; Laeng, Bruno & Nakauchi, Shigeki
(2018).
The differential effect of glowing appearance in the glare illusion: evidence from pupillometry.
-
Tørresen, Jim & Laeng, Bruno
(2018).
UiO/ROBIN – Toyohashi University of Technology/Japan seminar .
Show summary
Seminar with collaborators from University of Technology, Japan: Shigeki Nakauchi <https://www.tut.ac.jp/english/schools/faculty/cs/169.html> og Tetsuto Minami <https://www.tut.ac.jp/english/schools/faculty/eiiris/573.html> and their students.
-
Mæhlum Walle, Kjersti; Kyler, Hillary Lynn; Nordvik, Jan Egil; Becker, Frank & Laeng, Bruno
(2018).
Corrigendum to "Binocular rivalry after right-hemisphere stroke: Effects of attention impairment on perceptual dominance patterns" [Brain Cogn. 117 (2017) 84–96].
Brain and Cognition.
ISSN 0278-2626.
123,
p. 89–91.
doi:
10.1016/j.bandc.2018.03.001.
-
Sato, Fumiyaki; Laeng, Bruno; Nakauchi, Shigeki & Minami, Tetsuto
(2017).
Pupil dilation during perception of the Necker cube reflects the viewing-from-above bias.
-
Jo, Skaansar; Laeng, Bruno & Anne, Danielsen
(2017).
Pupil response reflects processing of microtiming in musical grooves: a study of musicians and non-musicians
.
-
Laeng, Bruno
(2017).
The pupil as a window to music's soul.
-
Bochynska, Agata & Laeng, Bruno
(2015).
Tracking down the path of memory. Eye scanpaths facilitate retrieval of visuospatial information.
-
Bochynska, Agata; Eifring, Halvor Bøyesen; Laeng, Bruno & Lobben, Marit
(2015).
The role of visual attention in the semantic processing of item, container and default numeral classifiers in Chinese.
-
Bochynska, Agata & Laeng, Bruno
(2015).
Re-enactment of eye movements’ sequences facilitates retrieval of visuospatial information.
-
Laeng, Bruno
(2015).
Blåtime.
Arkitektur N.
ISSN 1504-7628.
1,
p. 82–89.
-
Bochynska, Agata & Laeng, Bruno
(2014).
The Sequence Matters. An Experimental Study of the Functional Role of Eye Movements in Long-term Visuospatial Memory.
-
-
Benavent, S.A. de Rodez; Nygaard, Gro Owren; Tønnesen, Siren; Celius, Elisabeth Gulowsen; Landro, N. I. & Laeng, Bruno
(2013).
Pupillometry indicates increased cognitive effort in response to easy cognitive tasks in newly diagnosed MS patients.
Multiple Sclerosis.
ISSN 1352-4585.
19(7),
p. 988–989.
-
Chelnokova, Olga V; Laeng, Bruno; Riegels, Jeppe; Løseth, Guro Engvig; Eikemo, Marie Helene & Leknes, Siri Graff
(2013).
THE HUMAN OPIOID SYSTEM MEDIATES ATTENTION TO OTHERS' EYES.
Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience.
ISSN 0898-929X.
p. 216–216.
-
-
Specht, Karsten & Laeng, Bruno
(2011).
An Independent Component Analysis of fMRI data of grapheme-color synaesthesia.
-
Olsen, Bernt Ivar; Laeng, Bruno; Kristiansen, Kari-Ann & Hartvigsen, Gunnar
(2011).
Spatial Tasks on a Large, High-Resolution, Tiled Display: A Male Inferiority in Performance with a Mental Rotation Task.
-
Espeseth, Thomas; van de Pavert, Steven; Jynge, Slije; Sneve, Markus Handal & Laeng, Bruno
(2010).
The pupil dilates as a function of attentional effort in multiple object tracking.
-
Sørensen, Lin; Adolfsdottir, Steinunn; Laeng, Bruno; Lundervold, Astri & Plessen, Kerstin J.
(2010).
Regulation of emotion in children with ADHD - a longitudinal study. Development of an Emotional Stroop Test.
-
Leknes, Siri Graff & Laeng, Bruno
(2009).
Social touch: investigating the role of oxytocin for interactions in the hedonic experience of touch and emotion.
SFN Abstract Viewer/Itinerary Planner.
Show summary
Touch is a key means of interpersonal communication. The hormone oxytocin has been closely linked with affectionate touch. In this preliminary study, we investigate how altering the emotional expression and identity of visually perceived human faces may affect the hedonic experience of soft stroking touch. Conversely, the effects of social touch upon face perception are investigated. Finally, this study uses intranasal oxytocin administration (40IU) to elucidate the role of this hormone for social touch.
Images of angry, neutral and happy facial expressions were chosen from the Karolinska Directed Emotional Faces database. In addition, two types of “hybrid” faces that showed anger or happiness only in the lowest spatial frequencies (1-6 cycles/image) and a neutral expression in the rest of the bandwidth (7-128 cycles/image) were used. Faces in the five emotion conditions were of the same 20 men and 20 women and were matched for luminance. Images were displayed in a pseudorandomised order for 3 sec and accompanied by touch (soft strokes of 3cm/sec to the forearm) or control stimulation (70Hz vibration presented once/sec to the dorsum of the hand). To avoid bias, the experimenter performing touch and vibration stimuli wore a silk glove and was hidden from view. The outcome measures of this double-blind, placebo-controlled within-subjects study were pupil diameter and subjective ratings of touch and face perception. Three main hypotheses were tested in this preliminary investigation. 1) Socially relevant seen emotion affects perception of social touch. 2) Pupil size reflects the pleasantness and subjective relevance of social touch. 3) Social touch and oxytocin affect perception of human face stimuli. The significance of preliminary findings was assessed with one-tailed, paired t-tests.
As hypothesized, pilot data (N=9) showed an effect of socially relevant seen emotion on perception of touch pleasantness (but not touch intensity). When subjects viewed angry faces, touch pleasantness (6.0±0.4, mean±SD) was significantly lower than with neutral (6.2±0.4, p=0.033) or happy face stimuli (6.4±0.4, p=0.028). Overall, soft stroking was significantly more pleasant than the control stimulus (p=0.018) but both were equally intense (p=0.44) during oxytocin and placebo sessions (N=5). As expected, pupil size increased during pleasant, social touch relative to control stimulation (mean diameter difference 0.04±0.02 mm, p=0.032). Finally, there was a trend towards reduced ratings of perceived anger during social touch in the oxytocin session only (p=0.056; placebo session p=0.33), consistent with an anxiety-reducing effect of oxytocin and social touch.
-
Laeng, Bruno
(2009).
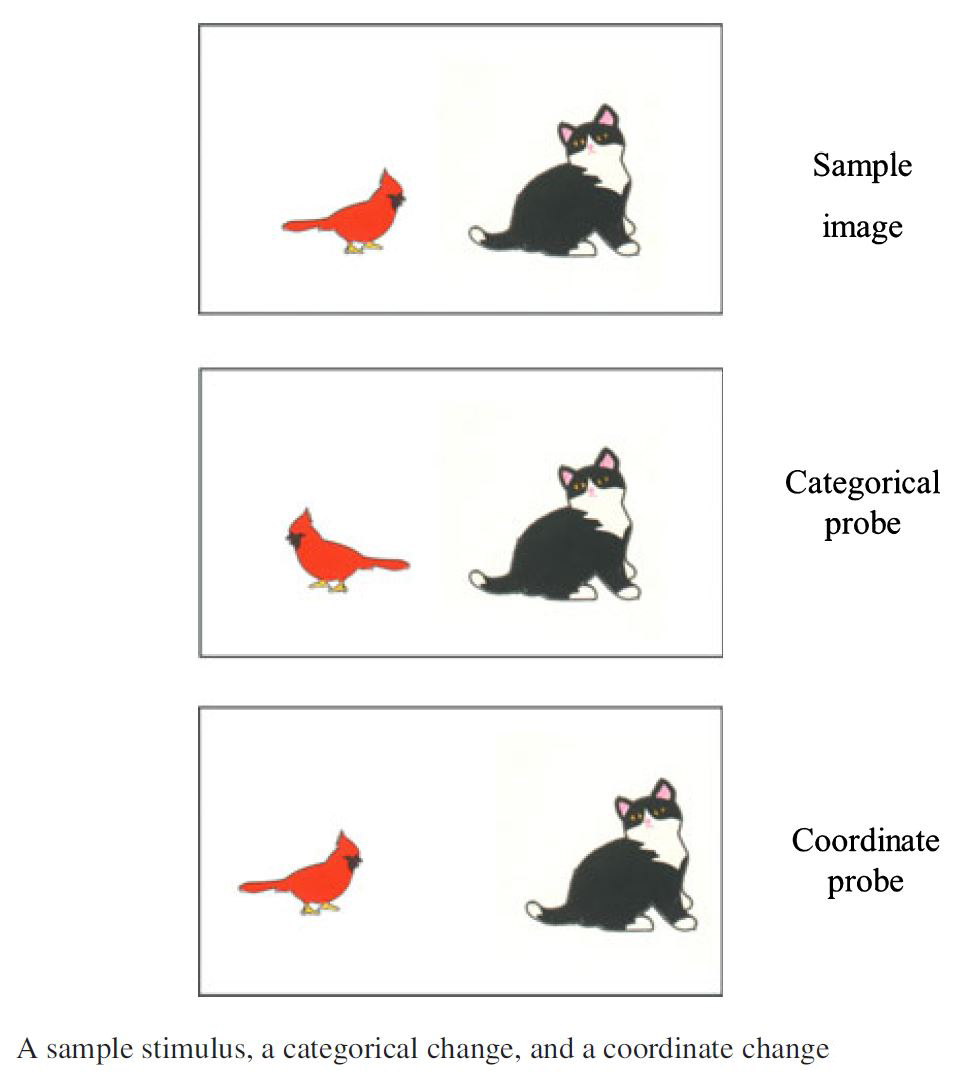
Processing coordinate and categorical spatial relations with different apertures of attention.
Cognitive Processing.
ISSN 1612-4782.
10,
p. S144–S144.
-
Olsen, Bernt Ivar; Laeng, Bruno; Kristiansen, Kari-Ann & Hartvigsen, Gunnar
(2009).
Spatial Tasks on a Large, High-Resolution Tiled Display: Females Mentally Rotate Large Objects Faster Than Men.
-
Postma, A & Laeng, Bruno
(2006).
New insights in categorical and coordinate processing of spatial relations.
Neuropsychologia.
ISSN 0028-3932.
44,
p. 1515–1518.
-
Halvorsen, Marianne; Wang, Catharina E.; Waterloo, Knut ; Eisemann, Martin ; Laeng, Bruno & Verplanken, Bas
(2006).
Depresjon og sårbarhets-prosjektet: Kognitiv unngåelse som sårbarhetsfaktor for tilbakevendende depresjon.
-
Laeng, Bruno; Specht, Karsten & Hugdahl, Kenneth
(2006).
A fMRI study of a grapheme-color synaesthete: The larger the color difference between ink and illusory colors, the more the visual areas are engaged.
-
Laeng, Bruno; Specht, Karsten & Hugdahl, Kenneth
(2006).
A fMRI study of a grapheme-colour synaesthete: The larger the colour difference between ink and illusory colours, the more the visual areas are engaged.
-
Øvervoll, Morten; Laeng, Bruno & Steinsvik, Oddmar Ole
(2005).
Learning 1500 pictures: memory for pictures is far from perfect, but the right hemisphere remembers better than the left.
-
-
Flaskerud, Ingvild & Laeng, Bruno
(2000).
Nordens Buddha. Emanuel Swedenborg (1699-1771.
-
Zelechowska, Agata; Jensenius, Alexander Refsum; Laeng, Bruno & Vuoskoski, Jonna Katariina
(2020).
Irresistible Movement: The Role of Musical Sound, Individual Differences and Listening Context in Movement Responses to Music.
Universitetet i Oslo.
Full text in Research Archive









.gif)



.gif)










.gif)